NMT历史上的今天
2017年10月11日,鲁东大学资源与环境工程学院傅金民利用NMT在Plant and soil上发表了标题为Application of Aspergillus aculeatus to rice roots reduces Cd concentration in grain的研究成果。

期刊:Plant and soil
主题:在水稻根部施用刺曲霉可降低谷物中的Cd浓度
标题:Application of Aspergillus aculeatus to rice roots reduces Cd concentration in grain
影响因子:3.306
检测指标:Cd2+流速
检测部位:水稻根部(距离根尖500μm)
Cd2+流实验处理方法:
三周龄的水稻幼苗,50uM镉处理、50uM镉+ A. aculeatus处理7/14天
Cd2+流实验测试液成份:
50 μMCdCl2, 0.5 mMKCl, 0.1 mM CaCl2, 0.1mMNaCl, 0.1mMMgCl2 and 0.3mM2-(Nmorpholino)ethane sulfonic acid (MES)
作者:鲁东大学资源与环境工程学院傅金民
英文摘要
‘Cd toxicity in rice’ events have resulted in vast public concern and uncertainty. Effective bioremediation could be accomplished via applying microbes that are capable of alleviating Cd content in rice grains.
Here, we investigated the effect of inoculating Aspergillus aculeatus on tolerance, uptake and transportation of Cd in rice cultivated in Cd contaminated growth medium.
A. aculeatus facilitated rice growth in Cd polluted growth medium and alleviated Cd toxic effects according to our observations on biomass, leaf and root length and grain yield. Cd accumulation analysis indicated that the plants which were inoculated with A. aculeatus exhibited minimum Cd level in all organs. Particularly in grain we observed a 40.5% reduction compared to the Cd only treated plants. Differences in Cd accumulation in rice inoculated with A. aculeatus might be attributed to the enhancement of cell wall-bound Cd, decreasing the Cd inorganic forms in roots, and inhibiting the expression of OsNRAMP5 and OsNRAMP1. A. aculeatus inoculation also led to minimum growth medium DTPA-Cd concentration, which possibly reduced the availability of the metals for plant uptake.
These results suggested that A. aculeatus might potentially be applicable to improve Cd tolerance and reduce Cd transportation in grains of rice.
中文摘要(谷歌机翻)
大米事件中的镉毒性已引起公众的广泛关注和不确定性。通过应用能够减轻稻米中Cd含量的微生物,可以实现有效的生物修复。
在这里,我们研究了接种刺曲霉对Cd污染的生长培养基中种植的水稻对Cd的耐受性,吸收和运输的影响。
根据我们对生物量,叶片和根长以及籽粒产量的观察,A。aculeatus促进了水稻在Cd污染的生长培养基中的生长,并减轻了Cd的毒性作用。镉的积累分析表明,接种了棘孢曲霉的植物在所有器官中都表现出最低的镉水平。与仅使用镉处理的植物相比,特别是在谷物中我们观察到减少了40.5%。接种A. aculeatus的水稻中Cd积累的差异可能归因于细胞壁结合的Cd的增强,根部中Cd无机形式的减少以及抑制OsNRAMP5和OsNRAMP1的表达。刺果曲霉的接种还导致生长培养基中DTPA-Cd的浓度降至最低,这可能会降低植物吸收金属的有效性。
这些结果表明,刺果曲霉具有提高Cd耐性和减少Cd在水稻籽粒中运输的潜力。
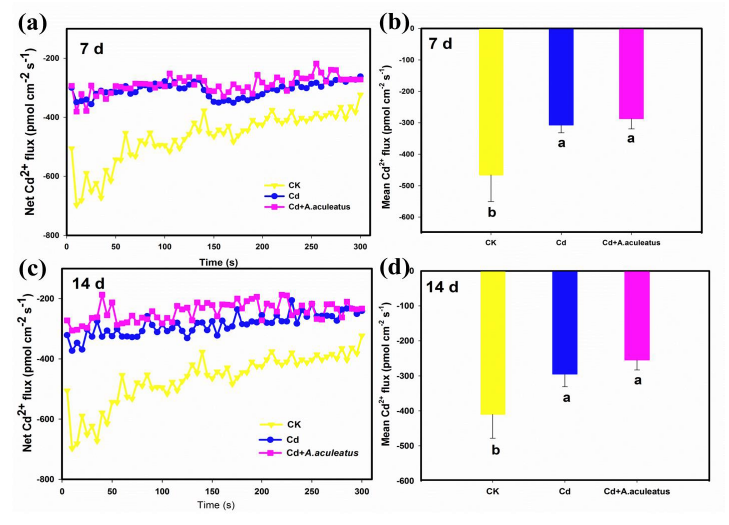
Supplementary Fig. 1 Effects of the Cd- resistant strain A. aculeatus on the net fluxes (a, c) and the mean fluxes (b, d) of Cd2+ in rice roots. Values are means ± SD. The different letters indicate the values that were significantly different at P < 0.05.
文章链接:https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007%2Fs11104-017-3465-9
